Glass And Acoustic Insulation
Acoustic power
Acoustic power can be expressed by its intensity I or its pressure P, measured in Watts per square metre or Pascals. It is common practice to measure sound by its level of pressure or intensity, against a logarithmic scale which starts at the threshold of hearing (I0, P0).
Sound intensity level
L1 = 10 log l/I0
Sound pressure level
L1 = 10 log P2/ P02= 20 log P/P0
The decibel (dB), is the unit
of measurement. Although the acoustic intensity of two or more sources increases by addition, the same is not true of the acoustic power.
Example
2 trumpets each producing a level of 80 dB together produce 83 dB, and not 160 dB.
Frequency
Sound arises from molecules vibrating in a gas, liquid or solid. The number of vibrations or soundwaves emitted per second is known as the frequency and is expressed in Hertz (Hz). The human ear is sensitive to sounds in the frequency range 16 Hz to 20000 Hz. Architectural acoustics generally concerns itself with the 50 Hz to 5 000 Hz range, which is divided into bands of frequencies or octaves. At each octave the frequency doubles. For more detailed analysis, 1/3 octaves may be used.
Weighted values
To account for the subjective nature of the human ear at different frequencies (low, medium and high-pitched sounds), sound pressure levels are measured against an A-weighted curve.
These levels, expressed in A-weighted decibels dBA, more accurately reflect noise or unwanted sound. Sound exposure meters can measure levels in dB or dBA.
The sound reduction index (r)
This index allows the sound absorbent properties of materials to be calculated and is measured in a laboratory. Measurements are taken in accordance with EN ISO 140, and represent the acoustic properties of an element (such as a window or partition) for each 1/3 octave band centred between the values 100 and 3 150 Hz (16 values). Further measurements may be taken at frequency ranges of 50 to 100 Hz and 3150 to 5000 Hz.
Calculations based on the 1/3 octave frequency bands enable the acoustic properties of an element to be expressed in different ways. These are defined in globally accepted values, by EN ISO 717-1, and adapted to two given noise spectra :
Pink noise
Index, where equal levels of sound power are applied across the entire spectrum of frequencies
Road traffic noise
Index is a good representation of how glazing attenuates road noise.
Using the rw index ( c ; c t r)
The acoustic insulation property of a building material is defined by an index representing the difference between internal and external noise levels. The acoustic insulation performance of a building element is the R sound reduction index. Designers use the R index for building materials to help achieve the specified noise reduction level.
Weighted reduction index rw
This is the most common method of rating sound insulation in buildings and building elements. It incorporates a weighted correction for the human ear and is expressed in dB. Calculation methods use a standard noise spectrum and are detailed in EN ISO 717-1.
Spectrum adaptation terms – c and ctr
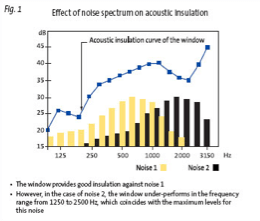
Depending on how a window is assembled and installed, it may under-perform at low, medium or high frequencies. Optimum performance can be achieved from a unit when it provides good
acoustic insulation at the frequencies where the noise is at its greatest. Good acoustic insulation against specific types of noise can also be achieved by modifying the type and composition of the glazing. Until recently, glazing specification has been based on a single performance figure, without taking all the characteristics of the noise source into account, which can sometimes lead to unwise investment and over-specification.
For this reason a common index has been created : Rw (C;Ctr ).
The correction Ctr should be used when the source of the noise in question is road traffic. For outside background noise it is better to use the correction C. Both corrections are generally negative and are deducted from the Rw to determine the noise reduction properties of a building element. They are provided by test laboratories and appear alongside the value for Rw.
Example
According to EN ISO 717-1 the formula is : Rw (C;Ctr) = 37 (-4;-9)
This means that the sound insulation value for a facade is 37 dB and is reduced by 9 dB for traffic noise.
In some countries the result can be indicated directly:
RA, tr = 28 dB, that is = 37-9 The same calculation can be applied for term C (pink noise):
RA = 33 dB, that is = 37-4.
This approach enables the designer to select the optimum window specification for the required application. This is further improved by comparing the sound reduction index R values of the window against the noise spectrum for each noise at one-third octave intervals.
The performance of glazing
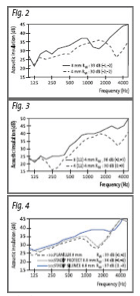
Each glass type and thickness has a critical frequency at which its sound reduction value is low. At this frequency, or coincidence resonance, it vibrates more easily and transmits noise more readily. The acoustic insulation performance of glass can be affected by as much as 10 to 15 dB.
For 4 mm monolithic glass, the critical frequency is 3 000 Hz, whilst for 13 mm thick plaster it is 3 200 Hz. By increasing the thickness of the glass, its coincidence resonance is displaced towards the lower frequencies. The glass would have to be 12 cm thick before the “hole” caused by the critical frequency dropped below 100 Hz and could therefore be ignored.
It is more difficult to provide effective acoustic insulation for facades subjected to high-intensity, low-frequency noise (such as road traffic). Until recently, the acoustic performance of glazing was improved mainly by increasing the thickness and asymmetry of glass panes in double-glazed units. In certain cases laminated safety glass would behave almost like monolithic glass of the same thickness . Today, with the exclusive development of acoustic PVB laminated glass, the critical frequency effect has been overcome. On average it is possible to improve performance by 1 to 3 dB compared to glass similar in type or thickness and above all to ensure uniform performance across a broader range of frequencies.
Acoustic performance comparisons
R index
The performance of a window cannot be determined from that of the glass element alone. The sound reduction index for a window can only be verified after testing the complete assembly. On the other hand it is advisable to match the glass type to the frame and type of pointing. Top-of-the-range glass such as Dualtherm Acoustic Laminates should be installed in high-performance frames.
The following table shows the Rw (C; Ctr) values of various glass types currently available on the market.
The last two columns give net acoustic insulation values RA and RA,tr (in dBA). The acoustic performance of double-glazed units is not affected by the thicker or laminated glass constituting the inner or outer pane.
However, due to the barometric effects on double-glazed units dualseal recommends that the thicker glass is used on the outer leaf of the unit. (see acoustic data on the product pages for more information)
Single-glazing