Installation
Glazing Method
The selection of a suitable and practicable glazing method depends on a variety of factors such as the size of the glass, the exposure and the type of framing material and system.
Glazing and fixing techniques must comply with the recommendations of BS 8000: 1990 Workmanship on building sites Part 7: Code of practice for glazing, BS 6262: 1982 Code of practice for glazing for buildings, and amendments plus those of the frame and sealant manufacturers and any recommendations featured in the DSG GLASS GUIDE. It is not the intention of this section to provide method statements on the various techniques of glazing, but to offer a general guide and introduction to the methods of glazing currently available. Diagrams are provided for illustration purposes only.
Glazing Blocks
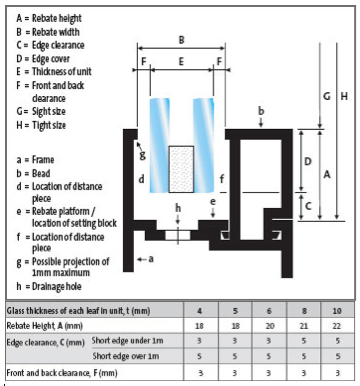
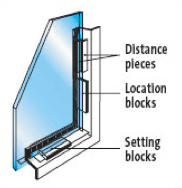
Setting blocks, location blocks and, where necessary, distance pieces must be used to provide support and adequate clearance between the glass and the frame.
The number and spacing of the blocks relates to the size of glass pane, framing system and conditions of use.
They should be of a resilient, nondegradable and non-absorbent material and should be able to accommodate the thermal expansion of the frame and glass without imposing stress on the glass.
SINGLE-GLAZING
Before glazing, check that the clearances are appropriate for the thickness and type of glass. If the glass is in direct contact with the framing materials, it could lead to breakage.
Care should be taken to avoid blocking drain holes or slots in drained framing systems.
Further details are given in BS 6262: 1982 and BS 8000 part 7: 1990. A new European Standard prEN ISO 14439 currently in preparation will advise on the function, requirement, materials and dimensions of glazing blocks.
SINGLE-GLAZING
BS 8000 part 7 recognises five main techniques for single glazing.
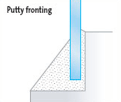
1. INTO REBATES WITHOUT BEADS
The glass sits in a rebate, held in place by a suitable glazing material, such as putty or a plastic-based compound, which then provides a weatherproof seal
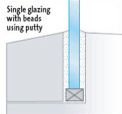
2. INTO REBATES WITH BEADS
As before the glass sits in a rebate but is held in place primarily by the beading. The glazing compounds provide the weather seal. The use of a bead permits a greater choice of glazing compounds.
Since they are not providing structural support to the glass, they can comprise a more flexible material and this can improve their performance as a weather seal.
Various compounds are available including putty, non-setting and two part rubberising compounds, and pre-formed strips or tapes.
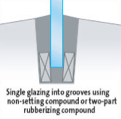
3. INTO GROOVES OR CHANNELS
This is sometimes also referred to as “pocket” or “shuffle” glazing. It is usually used for glazing into concrete, stone or timber frames with a rebate and bead at the cill only but it can also be modified to suit frames that have beads at the head and cill and grooves at the jambs. This glazing method can utilise gaskets, compounds or sealants.

4. USING STRUCTURAL GASKETS
Gaskets are used to hold the glass in a groove or rebate and to provide a weather seal.
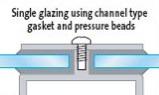
5. USING NON STRUCTURAL GASKETS
The glass is held in place by a combination of pressure beads and gaskets.
Double-Glazing
Prolonged contact with water will encourage the loss of adhesion between the sealant and glass. This can result in moisture vapour penetrating through the seal into the air cavity leading to the premature failure of the unit and formation of condensation inside the cavity.
Water can get into the rebate area from a number of sources including rainwater, window cleaning operations and condensation forming inside the framing section and also on the internal room-side surface of the glass.
The glazing system should either ensure that water cannot penetrate to They can include H-shaped, Y-shaped or single-sided gaskets.
To maximise the life of a sealed double-glazed unit, the preferred frame and glazing method must not allow moisture to collect at the edge of the unit seal.
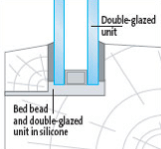
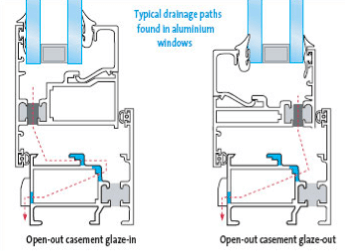
1. Non-Drained Systems
Referred to as “solid” or “fully bedded” framing systems. The edge-seal of the unit is protected from moisture by surrounding it in glazing compound and sealant.
It is important to ensure that there are not any gaps present in the sealant, which tend to trap any moisture that penetrates against the edge-seal.
They are typically and traditionally used in timber frames but sometimes also in steel frames.
2. Drained Systems
In drained systems it is acceptable for some moisture to penetrate the seal but for it not to be allowed to collect in the rebate.
The use of sloping rebate platform and / or drainage holes directs the moisture away from the edge-seal of the double-glazed unit. Some systems also have holes in the framing section to facilitate the movement of air around the perimeter of the unit, thereby encouraging rapid drying.
These are known as drained and ventilated systems. They can be applied to most types of frame including aluminium, PVC-U, steel and timber.
Fully drained or drained and ventilated systems are preferred. Dry glazing with pre-formed gaskets or wet glazing with compounds or sealants may be used, provided they are fully compatible with the edge-seal, glass and framing material.
No corrosive material can be used in the glazing system or in the maintenance of the system.
Sealant compounds used must be fully compatible with the glass, the unit seal and the framing material.
For example, acid based silicone compounds must not be used against the unit seal. All sealants must be applied and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Insertion of gaskets on site is usually carried out under pressure and it is important that this pressure does not exceed 5 kgf per linear centimetre.
The glazing system must be designed to provide adequate clearance around the unit in order to prevent glass-to-frame contact and to provide sufficient edge cover to retain the unit in position under the design loads.
The spacer bar and edge seal of a stepped-edge double-glazed unit exposed to sunlight (i.e. visible through the upper pane) must be protected from UV radiation by foil tape or a similar shading device if not factory-fitted.
It must also completely cover the edge seal of the unit to protect it from exposure to solar radiation.
This does not apply to specially ordered UV resistant silicone edge-sealed units.
Laminated Glass
Unless gasket glazing to drained and ventilated systems, particular care must be taken to protect the PVB interlayer against water ingress.
Prolonged contact with water can cause the interlayer to swell and ultimately lead to delamination.
The interlayer should also be protected from contact with compounds and products containing mineral or vegetable oils and unsuitable glazing compounds such as acid curing silicones. Laminated glass should be supported on all four edges and be free from holes, notches and cut-outs to
achieve its optimum performance and penetration resistance. All work on laminated glass should be
carried out under workshop conditions. It should not be attempted on site. In order to ensure maximum security, a security tape or adhesive (silicone) glazing method is recommended.
The depth of edge cover required depends on the strength of the framing material.
Further guidance can be found in BS 5357: Installation of security glazing or from the system manufacturer. British Standards and Building Regulations control the use and installation of glass in situations such as patent glazing and balustrading. A list of relevant British Standards is provided in Section 4 Standards and Regulations.
Fire resistant glasses must be glazed strictly in accordance with the tested method.
For more information on the use of security and fire resistant glazing contact the technical advice centre.